Keyboard shortcuts:
N/СпейсNext Slide
PPrevious Slide
OSlides Overview
ctrl+left clickZoom Element
If you want print version => add '
?print-pdf' at the end of slides URL (remove '#' fragment) and then print.
Like: https://wwwcourses.github.io/...CourseIntro.html?print-pdf
WebServices and JSON
Created by
WebServices Overview
WebServices Overview
- The term Web service (WS) is either:
- a service offered by an electronic device to another electronic device, communicating with each other via the World Wide Web, or
- a server running on a computer device, listening for requests at a particular port over a network, serving web documents (HTML, JSON, XML, images).
- In practice, a web service commonly provides an object-oriented Web-based interface to a database server, utilized for example by another Web server, or by a mobile app, that provides a user interface to the end-user.
- Many organizations that provide data in formatted HTML pages will also provide that data on their server as XML or JSON, often through a Web service to allow syndication.
- Reference: WebServices @wikipedia
RESTfull WebServices
- Representational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style that specifies constraints, such as uniform interface.
- These constraints helps a web service to induce desirable properties, such as performance, scalability, and modifiability, that enable services to work best on the Web
- Web service APIs that adhere to the REST architectural constraints are called RESTful APIs.
RESTful APIs
- HTTP-based RESTful APIs are defined with the following aspects:
- a base URI, such as http://api.example.com/
- standard HTTP methods (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE);
| HTTP method | Description |
|---|---|
| GET | used to read (or retrieve) a representation of a resource. |
| POST | most-often utilized to create new resources. |
| PUT | most-often utilized to update resources |
| DELETE | most-often utilized to delete resources. |
RESTful APIs with JSON
- RESTful services typically interact with data represented in JSON/XMl or other data-exchange format.
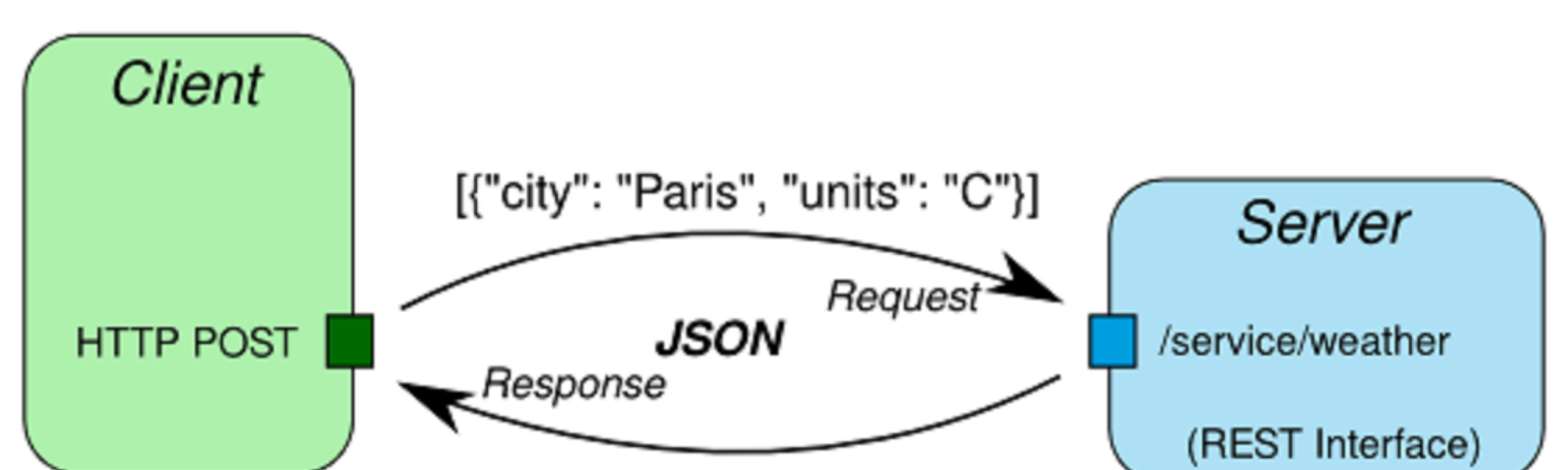
JSON Overview
JSON Overview
- JSON = JavaScript Object Notation
- A data-interchange format
- Language agnostic
- Proposed by Douglas Crockford in early 2000s
Why JSON
- Easy for humans (and the machines) to read and write
- Minimalistic syntax
- A strict subset of JavaScript (could be passed directly to
eval()) - JSON Schema is also defined
JSON vs XML
{
'fruits': ['apple', 'orange', 'banana'],
}
apple
orange
banane
- Useful resources:
- JSON Example
- JSON Conversions and Tools
Syntax
Syntax
JSON's basic data types
- Number
- a signed decimal number that may contain a fractional part
- String
- a sequence of zero or more Unicode characters, delimited by double quotation mark
- Boolean
- either of the values true or false
- Array
- an ordered list of zero or more values (may be of any type). Comma-separated elements in square brackets
- Object
- an unordered collection of
name:valuepairs, delimited by curly braces, where the names (also called keys) are strings. Pairs are separated by comma (trailing comma is not allowed)
JSON - example
{
"todos": [
{
"title": "Learn HTML",
"completed": true,
"id": 1
},
{
"title": "Learn CSS",
"completed": true,
"id": 2
},
{
"title": "Learn JS",
"completed": true,
"id": 3
}
]
}
JSON Validators
- JSONLint - online JSON Validator
- VSCode has built-in JSON support, including IntelliSense and validation
Parse and Stringify JSON
Parse and Stringify JSON
JSON to JS object (Parse JSON)
- It's important to understand that JSON is just a text format, not a JS data structure
- If we need to extract the information in a JSON string into respective JS data strucure, we must parse JSON string
const data = JSON.parse(jsonString);
// this is NOT a JS object, it's JUST a string
const jsonData = ` {
"title": "Learn HTML",
"completed": true,
"id": 1
}`;
console.log(typeof jsonData);
// parse json in rder to get the js object:
const data = JSON.parse(jsonData)
console.log(typeof data);
JS obj to JSON (stringify JSON)
- If we need to pass our JS data to some other program/server, we must convert the JS data into respective JSON string
var json = JSON.stringify(obj);
// this is a JS object
const data = {
"title": "Learn HTML",
"completed": true,
"id": 1
};
console.log(typeof data);
// let's convert it into JSON string:
const dataJSON = JSON.stringify(data)
console.log(typeof dataJSON);
Parse JSON from fetch()
- The
response.json()method returns a promise which resolves with the result of parsing the body text as JSON. - Note that despite the method being named json(), the result is not JSON but is instead the result of taking JSON as input and parsing it to produce a JavaScript object.
Parse JSON from fetch() - example
const url = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1';
fetch(url)
.then( response => response.json() )
.then( todoObj => console.log(todoObj.title) )
Public APIs returning JSON
Public APIs returning JSON
- List of public APIs
- Public APIs list on GitHub
- The Internet Chuck Norris Database API
- Open Trivia Database API
Exersices
Simple Jokes App
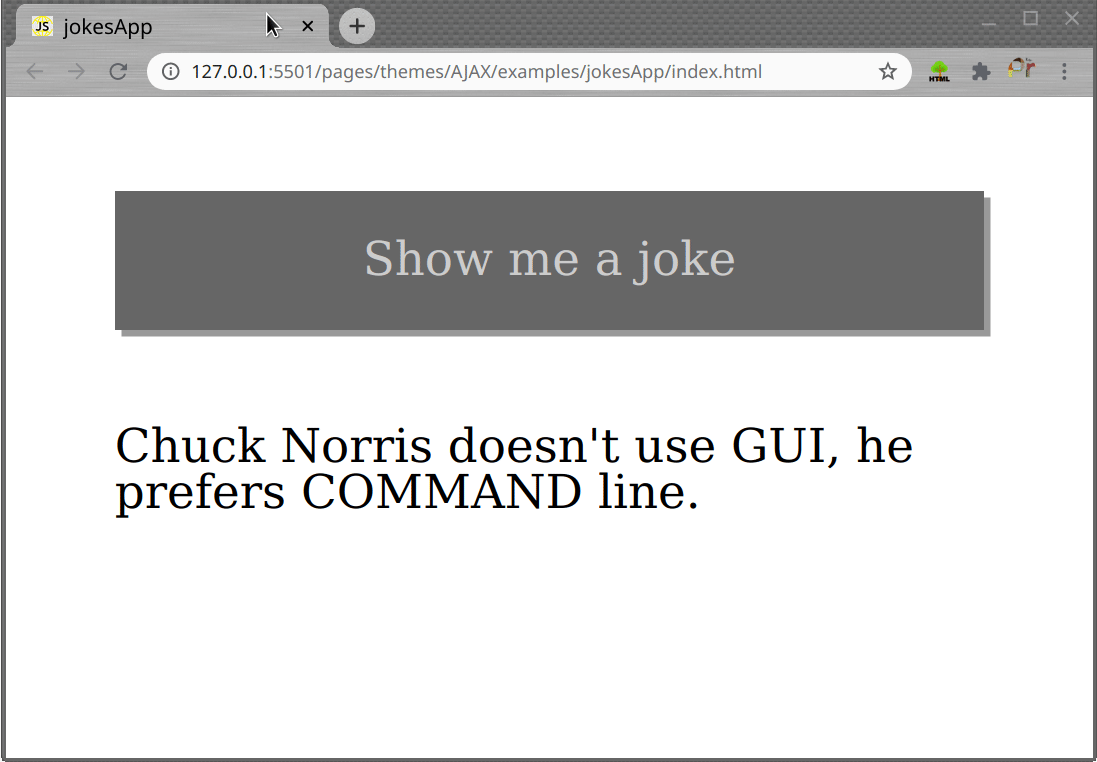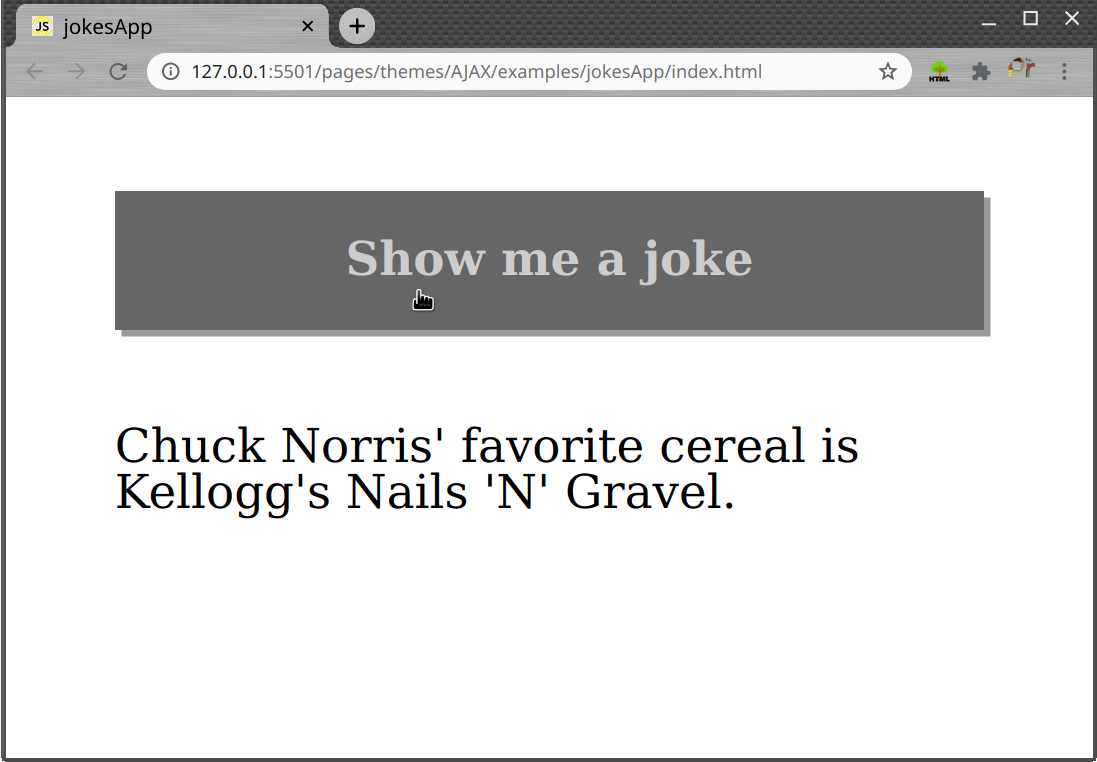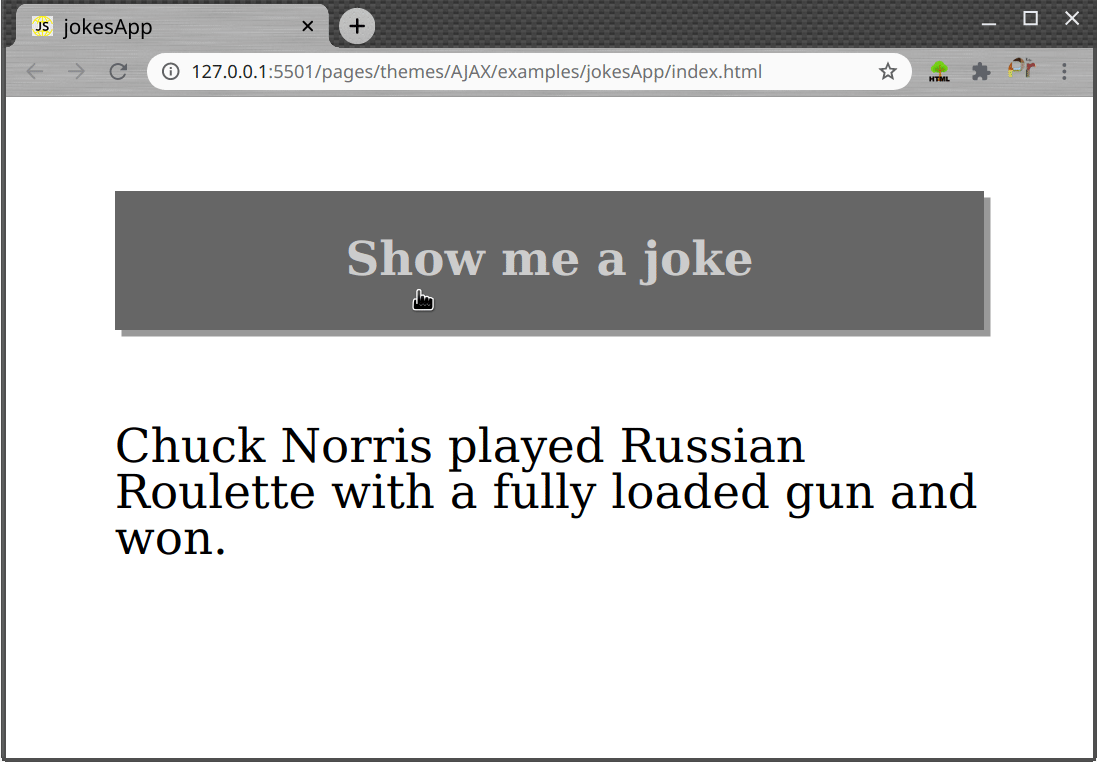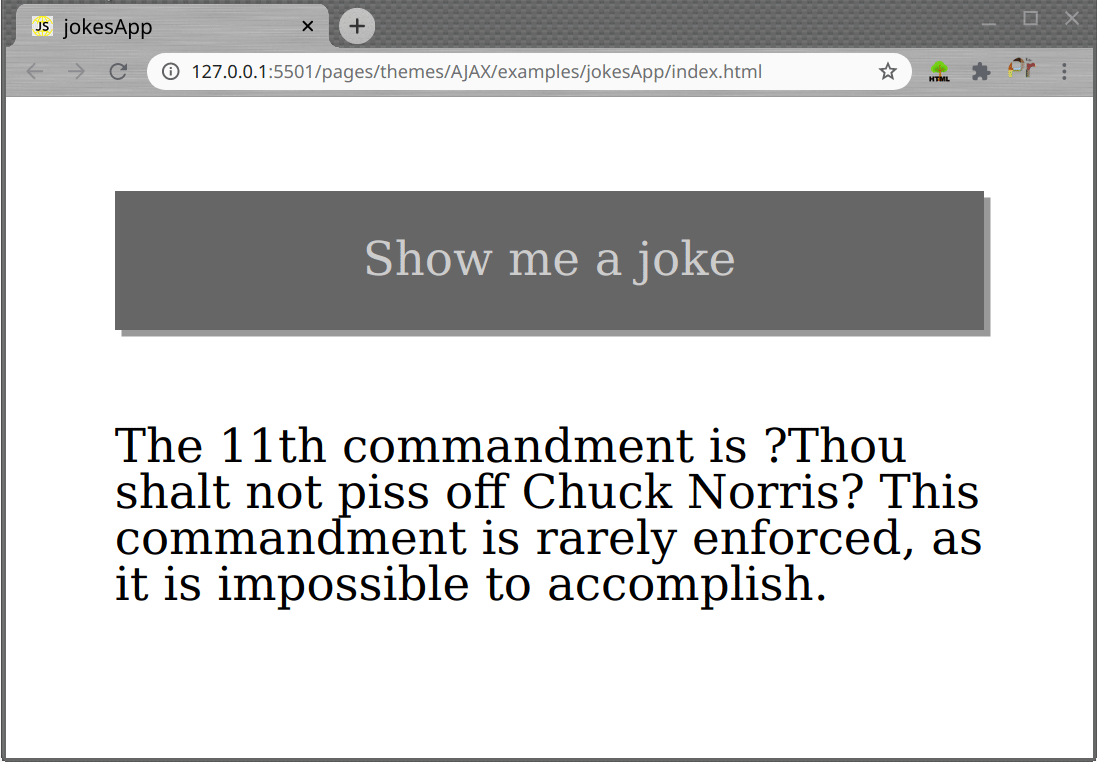
Task
- Create a page which shows random jokes on each button click, as shown in gif bellow.
Use thehttp://api.icndb.com/jokes/randomURL to fetch the joke data.
These slides are based on
customised version of
framework
