Keyboard shortcuts:
N/СпейсNext Slide
PPrevious Slide
OSlides Overview
ctrl+left clickZoom Element
If you want print version => add '
?print-pdf' at the end of slides URL (remove '#' fragment) and then print.
Like: https://wwwcourses.github.io/...CourseIntro.html?print-pdf
Map/Filter/Reduce Array methods
Created by
map()
map()
Overview
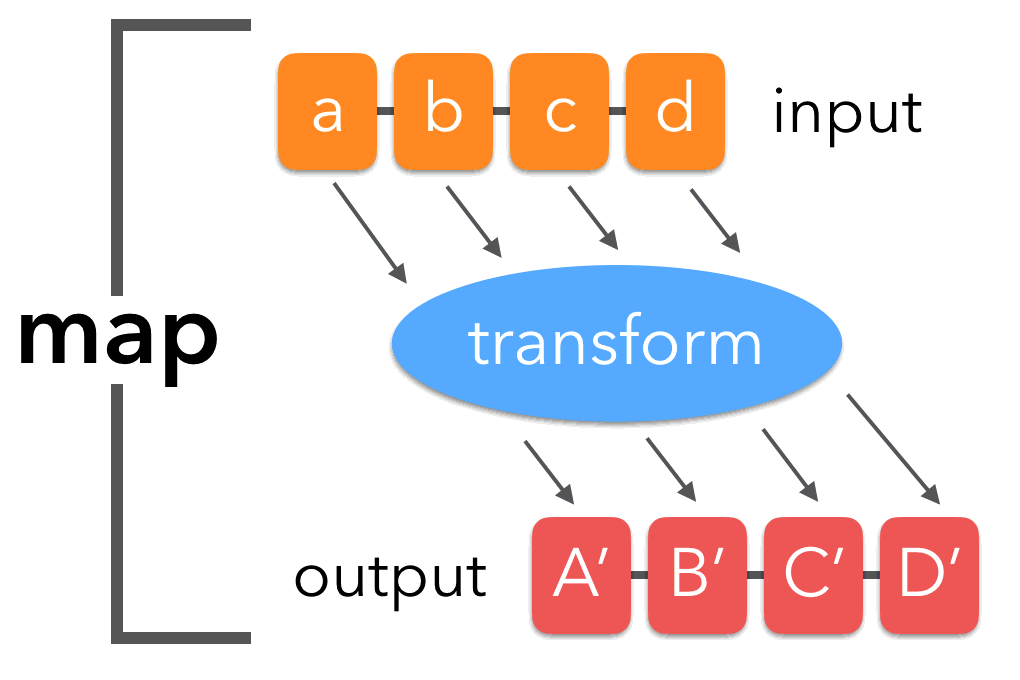
- The
map()method creates a new array with the results of calling a provided function on every element in the calling array.
Syntax 1
newArr = arr.map( callbackFn )
- callbackFn can be defined with arrow or with classic syntax
- callbackFn is called for every element of arr. Each time callbackFn executes it's returned value is added to newArray
- The callbackFn function accepts the following arguments:
- element: The current element being processed in the array.
- index: Optional. The index of the current element being processed in the array.
- array: OptionalThe array map was called upon.
- Reference: map @mdn
let input = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
let output = input.map((e,i,arr)=>{console.log(e, i, arr)})
//a 0 [ 'a', 'b', 'c' ]
//b 1 [ 'a', 'b', 'c' ]
//c 2 [ 'a', 'b', 'c' ]
Examples
let input = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'];
let output = input.map( e=>e.toUpperCase() )
console.log(`input: ${input}`);
console.log(`output: ${output}`);
//input: a,b,c,d
//output: A,B,C,D
let input = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'];
let output = input.map( function(e){
return e.toUpperCase()
} )
console.log(`input: ${input}`);
console.log(`output: ${output}`);
//input: a,b,c,d
//output: A,B,C,D
Example - using array index in callbackFn
let input = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
let output = input.map((e,i)=>e.toUpperCase()+i)
console.log(output);
// [ 'A0', 'B1', 'C2' ]
TASK_1:
// TASK: from 'cities' array generate a new array 'cityNames' which will contain only the names of the cities
let cities = [
{name: 'Sofia', population: 1_236_000},
{name: 'Plovdiv', population: 343_424 },
{name: 'Burgas', population: 202_766},
{name: 'Varna', population: 335_177},
];
// YOUR CODE HERE:
// TEST:
console.log(cityNames);
// EXPECTED OUTPUT:
// [ 'Sofia', 'Plovdiv', 'Burgas', 'Varna' ]
TASK_2
// TASK: from 'cities' array generate a new array 'bgCityNames' which will contain only the names
// of the cities, but mapped to their Bulgarian equivalent
let dict = {
'Sofia' : 'София',
'Plovdiv' : 'Пловдив',
'Burgas' : 'Бургас',
'Varna' : 'Варна'
}
let cities = [
{name: 'Sofia', population: 1_236_000},
{name: 'Plovdiv', population: 343_424 },
{name: 'Burgas', population: 202_766},
{name: 'Varna', population: 335_177},
];
// YOUR CODE HERE:
// TEST:
console.log(bgCityNames);
// EXPECTED OUTPUT:
// [ 'София', 'Пловдив', 'Бургас', 'Варна' ]
filter()
filter()
Overview
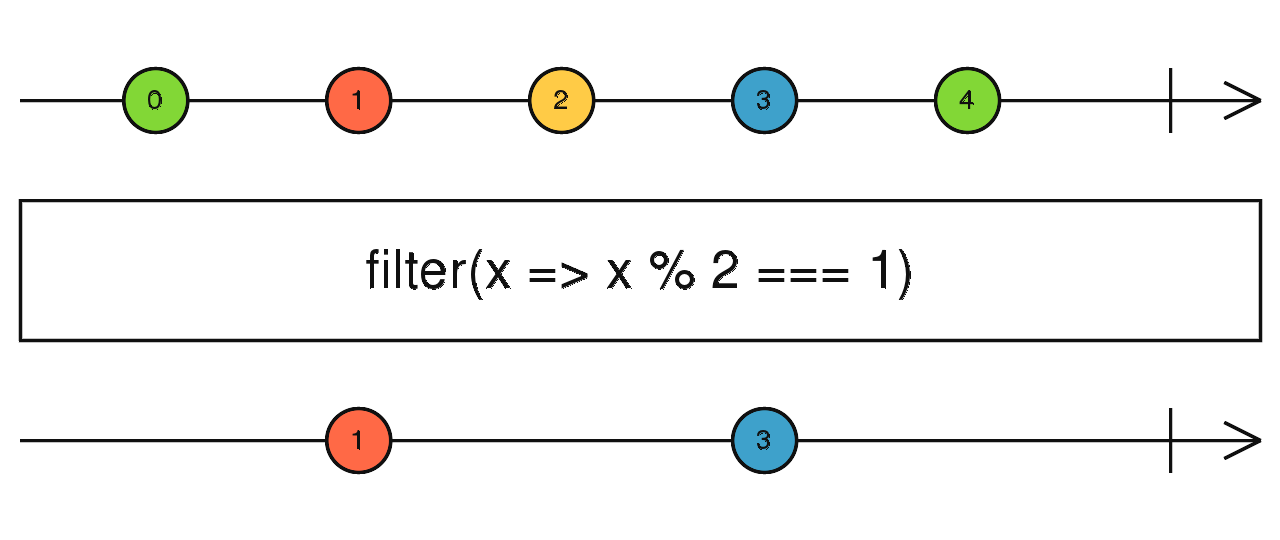
- The
filter()method creates a new array with all elements that pass the test implemented by the provided function. - I.e. the resulting array will contain only the input elements, for each the provided function will return
truevalue. - Reference: filter @mdn
Example
let input = [0,1,2,3,4];
let output = input.filter( x=>x%2);
console.log(`input: ${input}`);
console.log(`output: ${output}`);
Task
// TASK: filter only cities which population is greater than 340_000
let cities = [
{name: 'Sofia', population: 1_236_000},
{name: 'Plovdiv', population: 343_424 },
{name: 'Burgas', population: 202_766},
{name: 'Varna', population: 335_177},
];
// YOUR CODE HERE:
// TEST:
console.log(filtered);
// EXPECTED OUTPUT:
// [
// { name: 'Sofia', population: 1236000 },
// { name: 'Plovdiv', population: 343424 }
// ]
reduce()
reduce()
Overview
- The
reduce()method executes the provided reducer function on each element of the array, resulting in a single output value. - Reference: reduce @mdn
let value = arr.reduce(callbackFn)
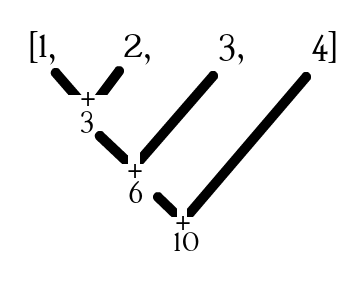
let input = [1,2,3,4];
let output = input.reduce( (acc, curr)=> {
console.log(acc,curr)
return acc+curr;
} );
console.log(`output: ${output}`);
// OUTPUT
// 1 2
// 3 3
// 6 4
// output: 10
A note for acc initial value
let value = arr.reduce( (acc, curr)=>{...}, initialValue );
- initialValue: Optional. A value to which
accis initialized the first time the callback is called. - If initialValue is specified, that also causes
currto be initialized to the first value in the array. - If initialValue is not specified,
accis initialized to the first value in the array, andcurris initialized to the second value in the array.
let input = [1,2,3,4];
let output = input.reduce( (acc, curr)=> {
console.log(acc,curr)
return acc+curr;
}, 0 );
console.log(`output: ${output}`);
// OUTPUT:
// 0 1
// 1 2
// 3 3
// 6 4
// output: 10
Example: sum of array's even numbers
- Using reduce() only - difficult to read and write.
let input = [1,2,3,4];
let output = input.reduce( (acc, curr)=> curr%2==0?acc+curr:acc, 0);
console.log(`output: ${output}`);
- Using filter().reduce() - better approach:
let input = [1,2,3,4];
let output = input.filter(el=>el%2==0).reduce((acc,curr)=>acc+curr)
console.log(`output: ${output}`);
Exercises
Task: filterWordsStartingWithLetter
description
- Given is the next Douglas Adams quote:
A common mistake that people make when trying to design something completely foolproof is to underestimate the ingenuity of complete fools.
- Make a program, which will write in the console only the words that starts with letter 't' and are longer than 2 symbols
that
trying
the
- Hint: to split a string into array of words you can use the String.prototype.split() method
Task: sumOfSquaresOfEvenNumbers
description
- Given is the next array of numbers:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] - Write a program which will output in the console the sum of the squares of even numbers
220
Task: calcProductsPrices
- The task is given in next template file. You can view the raw code by clicking on "view raw" in bottom-right corner
Task: mapArrayOfObjects
- The task is given in next template file. You can view the raw code by clicking on "view raw" in bottom-right corner
Task: getCityNameWithMinimalPopulation
- The task is given in next template file. You can view the raw code by clicking on "view raw" in bottom-right corner
Task: analyze groupProductsByCategory
- Analyze next approaches used to group products by category.
- Make sure you understand all of them.
These slides are based on
customised version of
framework
