If you want print version => add '
?print-pdf' at the end of slides URL (remove '#' fragment) and then print.
Like: https://wwwcourses.github.io/...CourseIntro.html?print-pdf
Created for

Relational DB Model Overview
Relational DB Model Overview
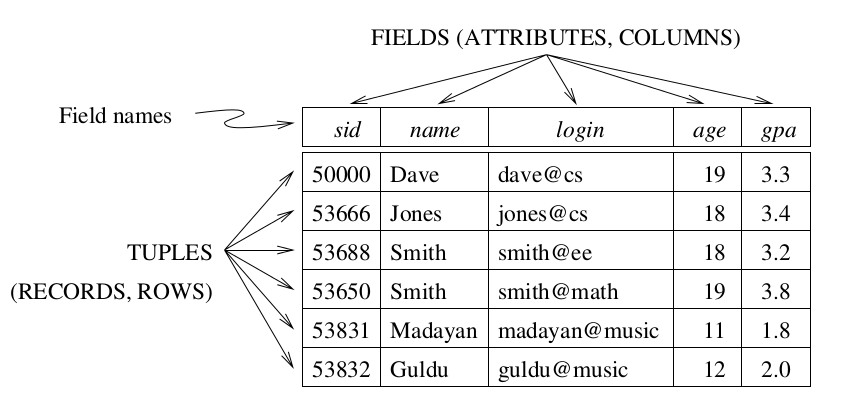
Definition
- A database is a collection of one or more tables, where each table is a relation between rows and columns.
- A relation consists of a relation schema and a relation instance.
- Relation instance - a table with rows and columns.
- Relation schema - describes the column heads for the table.
Key Concepts
- Relational DataBase
- A collection of tables, with related data.
- Tables - represents a Relation.
- Table and relations are synonymous in DB context.
- A relation is different from relationship between tables.
- A table consists of rows and columns, like a simple spreadsheet.
- Each table is a set of unique rows.
- Row (Tuple, Record)
- Represents a collection of related values (characteristic) of an entity.
- Column (Field, Attribute )
- One column contains data of one and the same type, as defined in schema.
Key Concepts
Tables Relationships
- One to one relationship
- Example: Customer -> Address
- One to Many/Many to One relationship
- Example: Customer -> Orders
- Many to Many relationship
- Examples: Orders -> Items
- Self Referencing relationship
- Customer -> Customer (like in referral program)
These concepts will be discussed further.
ExampleDatabase

Example Table
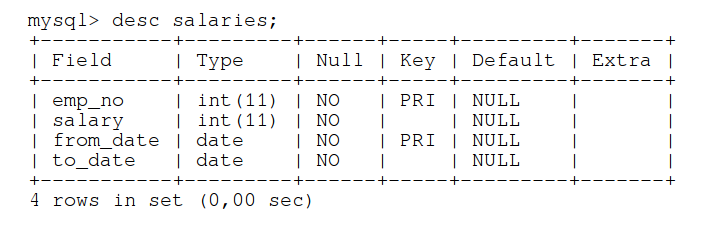
Popular Relationship Database Management System (RDBMS)
- Commercial:
- Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, SAP SyBase
- Free (under GPL)
- MySQL/MariaDB, PostgreSQL, SQLite
Setup MySQL
Setup MySQL
Install on Windows
- Installing MySQL on Microsoft Windows @https://dev.mysql.com/
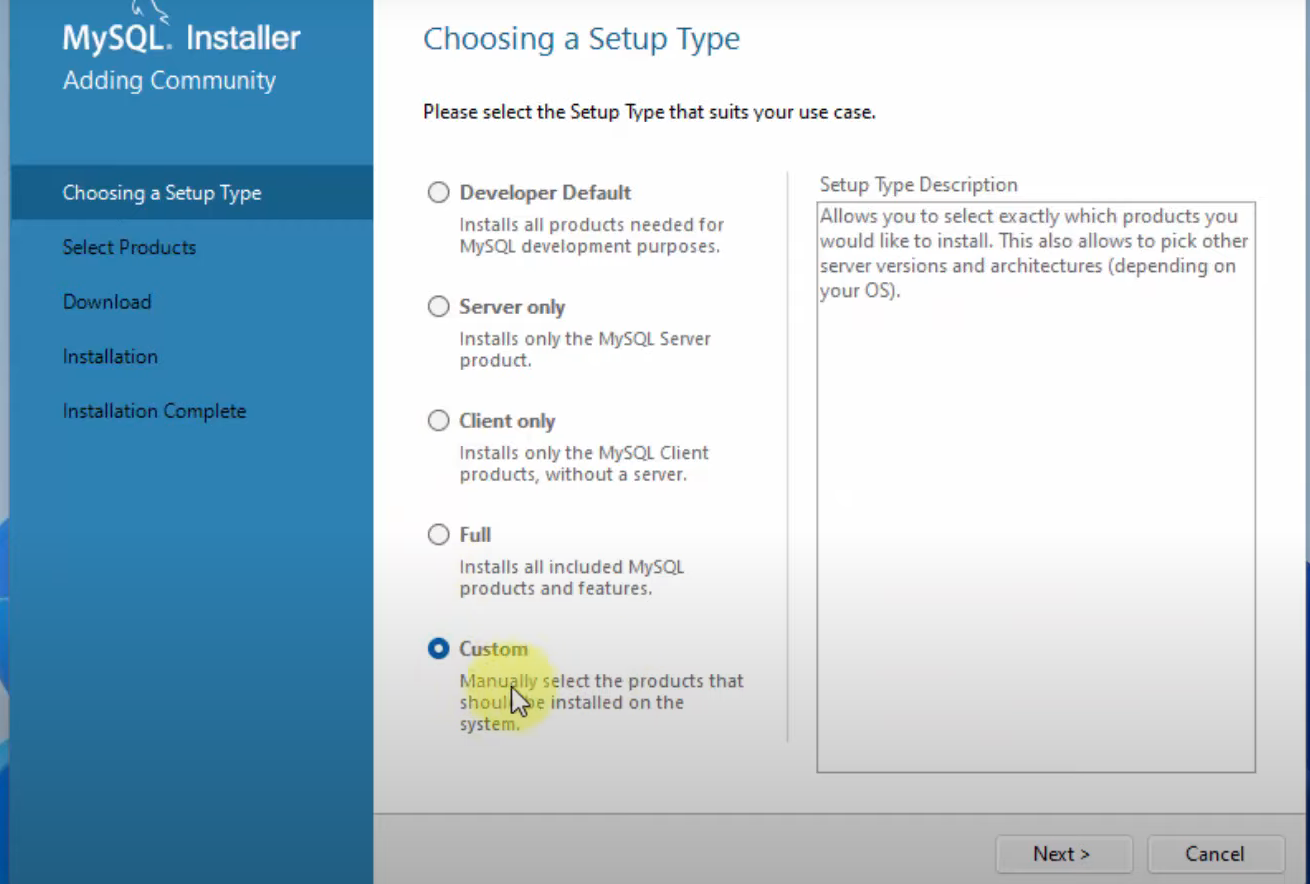
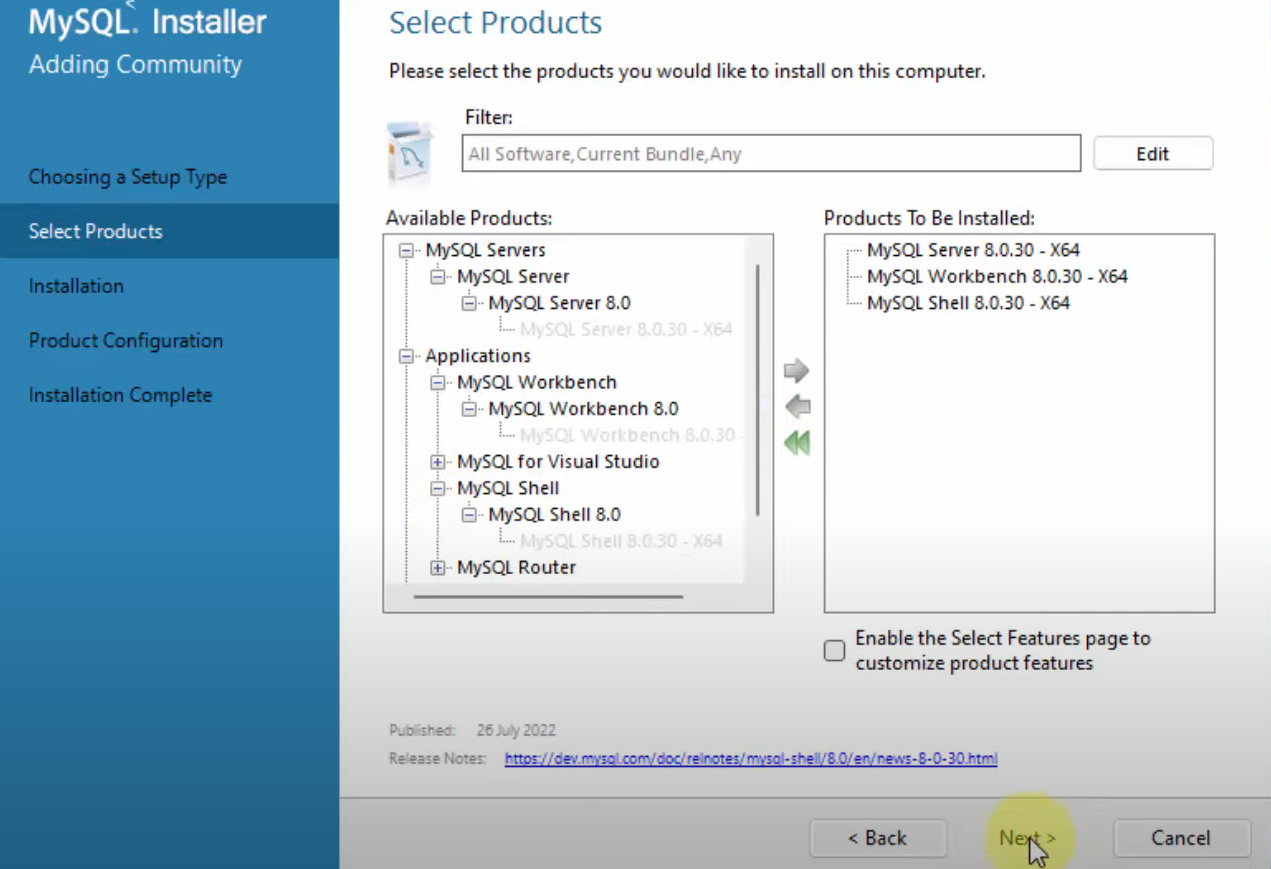
- For start we need only MySQl Server, MySQL Workbench and MySQL Shell , so on "Choosing a Setup Type" window select "Custom".
- reference: 2.3.3.1 MySQL Installer Initial Setup
Install on Windows - choose Setup Type
Install on Windows - Select Products
Install on Windows - Setup PATH for MySQL Tools
- On the Windows desktop, right-click the My Computer icon, and select Properties.
- Next select the Advanced tab from the System Properties menu that appears, and click the Environment Variables button.
- Under System Variables, select Path, and then click the Edit button. The Edit System Variable dialogue should appear.
- Place your cursor at the end of the text appearing in the space marked Variable Value. (Use the End key to ensure that your cursor is positioned at the very end of the text in this space.) Then enter the complete path name of your MySQL bin directory (for example, C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin)
- Reference: Customizing the PATH for MySQL Tools
Install on MacOS
Install on Linux
- Installing MySQL on Linux @https://dev.mysql.com/
- APT repos for all mysql-apt-config versions: https://repo.mysql.com/apt/ubuntu/pool/mysql-apt-config/m/mysql-apt-config/
- If you have problems on old linux version, you can try installing MariaDB
- https://downloads.mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories
- Check the installation:
systemctl status mysql
# ● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.2.38 database server
# Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
# Drop-In: /etc/systemd/system/mariadb.service.d
# └─migrated-from-my.cnf-settings.conf
MySQL Workbench
- MySQL Workbench is a unified visual tool for database architects, developers, and DBAs.
- Official site: www.mysql.com/products/workbench
- If after installation of mysql server you don't have MySQL Workbench, you can download it from:
- Download MySQL Workbench
mycli (optional)
mycli: A Terminal Client for MySQL with AutoCompletion and Syntax Highlighting.
Requires pythonTest the installations
Test the installations
- Open new Terminal (Command Prompt) and write next commands:
- If you receive error like: "mysql is not recognized as an internal or external command...", then check that you have added MySQL bin folder to System Variables=>Path.
- Reference: Customizing the PATH for MySQL Tools
### the client:
mysql --version
# mysql Ver 14.14 Distrib 5.7.11, for Linux (x86_64) using EditLine wrapper
### the server:
mysqld --version
# mysqld Ver 5.7.11 for Linux on x86_64 (MySQL Community Server (GPL))
Start/stop MySQL Server
Start/stop MySQL Server
Windows
- Open Run Window by Winkey + R
- Type services.msc
- Search MySQL service based on version installed.
- Click stop, start or restart the service option.
- Or you can start/stop MySQL from the command prompt:
- Reference: Starting MySQL as a Windows Service
C:\> "C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin\mysqld"
C:\> "C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin\mysqladmin" -u root shutdown
Linux
service mysql start
service mysql stop
service mysql restart
- Or if you have the old init.d
/etc/init.d/mysqld start
/etc/init.d/mysqld stop
/etc/init.d/mysqld restart
Connect to MySQL Server
Connect to MySQL Server
MySQL client
# connect to local mysql, using the root account:
mysql -u root -p
# Enter password:
# ...
# You should see something like:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 9
Server version: 8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1 (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
MySQL server - where my DB are stored?
- All MySQL databases are stored in directories inside a MySQL DATADIR directory.
- E.g. myExampleDB’s files would be stored inside ‘$DATADIR/myExampleDB’ directory.
- MySQl DATADIR is specified in the config file, but can be easily retrieved by:
mariadb root@localhost:(none)> select @@datadir
+-----------------+
| @@datadir |
|-----------------|
| /var/lib/mysql/ |
+-----------------+
1 row in set
Time: 0.002s
RDBMS - Basic Concepts
RDBMS - Basic Concepts
Data Definition Language (DDl)
- DDL helps you to define the database structure or schema
- Some common DDL Commands are
- CREATE, ALTER, DROP, TRUNCATE, etc.
- Changes are saved in the database immediately and permanently.
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
- The DML is the programming language used to express operations that interrogate or update the data in the database
- DML commands are used to manage the data stored in the database, like
- INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, MERGE, CALL, etc.
SQL Introduction
SQL Introduction
What is SQL?
- SQLStructuredQueryLanguage
- The standard language for relational database management systems.
- Not a procedural language(C, Java etc.).
- A declarative language!
- Tell with SQL what you want, instead of telling the system how to get it.
- Case insensitive!
SQL statements and queries
- SQL provides a set of commands you can use to query or manipulate the DB.
- SQL is case insensitive.
show databases;andSHOW DATABASES;are the same.- Database and table names are not case sensitive in Windows, but are case sensitive in most varieties of Unix or Linux.
desc mysql.user;will work butdesc mysql.USER;will return an error ((1146, "Table 'mysql.USER' doesn't exist")) on Linux/MacOS- Some RDBMS require a semicolon at the end of each SQL statement.
Example SQL commands
SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE
INSERT INTO, CREATE DATABASE, ALTER DATABASE
CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE
CREATE INDEX, DROP INDEX
Manage databases
Manage databases
List/Create/Delete/ databases
### List all databases
## only those databases for which the user have some kind of privilege (or if the user have the global SHOW DATABASES privilege)
SHOW DATABASES
### Create a database
CREATE DATABASE employees;
### Delete a database
DROP DATABASE employees;
### Selecting a Database
## Before performing any table manipulations, you need to select the database on which they will be performed
USE employees;
Import database (Setup Test Database)
- Download the test db and load it
- Employees Sample Database
git clone https://github.com/datacharmer/test_db/
cd test.db
mysql -u root -p < employees.sql
# Enter password:
# INFO
# CREATING DATABASE STRUCTURE
# INFO
# ...
Export DB to external sql file:
mysqldump -u username -p databasename > filename.sql
- Reference: mysqldump — A Database Backup Program
Manage users
Manage users
List All Users in a MySQL Database Server
- All mysql users are stored into
mysql.usertable
SELECT user,host FROM mysql.user;
Create a New User
CREATE USER 'employees_db_admin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '1234';
If user exists, an error will be thrown. To prevent this error we can use:
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'employees_db_admin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '1234';
Delete user
DROP USER 'employees_db_admin'@'localhost';
If user did not exists, an error will be thrown. To prevent this error we can use:
DROP USER IF EXISTS 'employees_db_admin'@'localhost';
User privileges types
- ALL PRIVILEGES- this would allow a MySQL users all access to a designated database (or if no database is selected, across the system)
- CREATE- allows them to create new tables or databases
- DROP- allows them to them to delete tables or databases
- DELETE- allows them to delete rows from tables
- INSERT- allows them to insert rows into tables
- SELECT- allows them to use the Select command to read through databases
- UPDATE- allow them to update table rows
- GRANT OPTION- allows them to grant or remove other users' privileges
Grant privileges to a user
GRANT [type of permission]
ON [database name].[table name]
TO ‘[username]’@'host’;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON employees.* TO 'employees_db_admin'@'localhost';
Note, that asterisk (*) means all (tables, databases, ...)
Revoke privileges
REVOKE [type of permission]
ON [database name].[table name]
FROM ‘[username]’@'host’;
REVOKE [type of permission] ON [database name].[table name] FROM ‘[username]’@‘localhost’;Reload all the privileges
Always be sure to reload all the privileges.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
How to Reset the Root Password
Reset the Root Password on Ubuntu based linux, step-by-step:
# stop mysql service
sudo systemctl stop mysql
# if you don't have '/var/run/mysqld' create it with proper user wrights:
sudo mkdir -p /var/run/mysqld
sudo chown mysql:mysql /var/run/mysqld
# start the server, passwordless
sudo /usr/sbin/mysqld --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking &
# connect as root without password:
mysql -u root
# now in mysql shell, run next commands
# do not forget to change the password '1234' with yours
> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
> USE mysql;
> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '1234';
> quit
Reference
Manage Tables
Manage Tables
CREATE TABLE - minimal syntax
CREATE TABLE table_name(
column_name1 data_type,
column_name2 data_type,
....
);
- If identifiers for database, table, column and other, contains special characters or is a reserved word you have to put them in backticks (``).
CREATE TABLE - example
CREATE TABLE artist (
artist_id SMALLINT(5) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
fname VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,
lname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (artist_id)
);
Results in:
Query OK, 0 rows affected
Time: 0.280s
If table exists an error will be thrown!
Show CREATE TABLE
# '\G' modifier is used instead of ';' to display wide results in vertical form
show CREATE TABLE artist\G
Results in:
***************************[ 1. row ]***************************
Table | artist
Create Table | CREATE TABLE `artist` (
`artist_id` smallint(5) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
`fname` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`lname` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`artist_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1
This allows us to see the create statement that MySQL engine had used. It shows even the default options, which we did not state explicitly.
SHOW TABLES
- We can list all tables in a DB with:
SHOW TABLES;
Results in:
+----------------------+
| Tables_in_music_db |
|----------------------|
| artist |
+----------------------+
DESC table
- To show the structure of a table:
DESC artist;
Results in:
+-----------+-------------+--------+-------+-----------+---------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
|-----------+-------------+--------+-------+-----------+---------|
| artist_id | smallint(5) | NO | PRI | 0 | |
| fname | varchar(20) | YES | | <null> | |
| lname | varchar(20) | NO | | <null> | |
+-----------+-------------+--------+-------+-----------+---------+
DROP TABLE
- To delete a table:
DROP TABLE artist;
If table do not exists, an error is thrown:
ERROR 1051 (42S02): Unknown table 'music_db.artist'
Alter tables
Alter tables
Add column
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD new_column_name column_definition
[ FIRST | AFTER column_name ]; # optional
ALTER TABLE artist
ADD birth_date TINYINT
AFTER lname;
Remove column
ALTER TABLE artist DROP birth_date;

